Le Corbusier, with his birth name Charles Edouard Jeanneret, was born on October 6, 1887, in a small town in Switzerland. Although we know him for his architecture, he is also an urbanist, furniture designer, sculptor, painter and writer. His innovative ideas and design principles have not only transformed the architecture field but also inspired generations of architects and designers.
From the very first years of his childhood, he developed a deep passion for architecture. His education and early works paved the way for his remarkable architectural ideas and principles and laid the foundation for his career.
In this article, we will take a glance at the life, education and principles of the architect as well as his architectural philosophy. Furthermore, we’ll examine the famous Le Corbusier buildings.
Early Life and Education
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret received a traditional education in Switzerland. He enrolled in an art school after he started to work with his father. His real education came from explorations and observations of natural and built environments.
During the art school, he was interested in the Arts and Crafts movement. He won a watch design competition where he applied with a cubist design. This was his first significant achievement as well as a prolog of future successes.
Le Corbusier’s formal architecture education began in 1900 by enrolling at the École d’Art in La Chaux-de-Fonds, Switzerland. This school provided him with opportunities of studying under renowned architects, such as Charles L’Eplattenier.
Here, he developed his design principles and technical skills, as well as deeply worked on architectural history. He also gained the mastery to balance functionality with aesthetic appeal.
Alongside the classroom, Corbusier learned from technical travels. He observed and analyzed different architectural styles, from classical to modern. These experiences made his perspective richer and allowed him to create a notable architectural understanding.
In the next part, we will focus on Corbusier’s career.
Career
An architect should travel, explore and analyze different environments and structures for his vocational development. Corbusier, with this consciousness, held an east tour in 1907 which would last for 4 years.
He visited the Mediterranean and Greek Islands, the Balkans, and the lands adorned with Ottoman architecture, meanwhile, he took notes. According to the architect, this trip was one of the most important stages of his architectural career.
In 1908, he started working with Auguste Perret, one of the pioneers of the use of reinforced concrete in architecture. Perret, the designer of the first reinforced concrete temple built in the world, taught Corbusier the specifics of using reinforced concrete in architecture.
While Corbusier gained this experience in Paris, he also had the opportunity to get to know the city’s culture and architecture better.
Affected by the natural and sculptural appeal of concrete on the facades, Corbusier had close contact with the “Deutscher Werkbund” in Germany to understand reinforced concrete better.
(Footnote: Deutsche Werkbund is an association of artists, craftsmen, designers and industrialists who came together in Germany in 1907. The union has contributed to the establishment of Bauhaus, the development and standardization of modern architecture.)
Dom-ino House
Le Corbusier predicted that the First World War would end one day. Then, there would be an urgent housing need when cities started to be reconstructed after the war.
He searched for a solution to solve this upcoming housing need in the most economical and rational way. Corbusier conducting experimental studies on this problem designed his first important building known as the Dom-ino House In 1915.
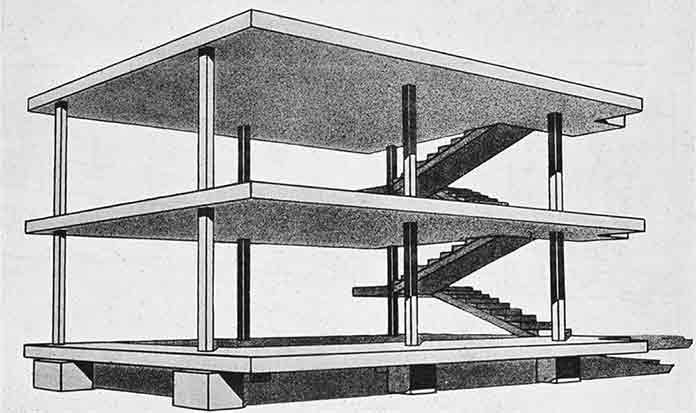
The structure that rises on an open plan and 6 thin reinforced concrete columns generated one of the fundamentals of Le Corbusier style.
Thanks to the structures with open plan setup, the location of the walls and partitions could be changed. This feature coincided with the principles of flexibility and pragmatism in modern architecture.
Dom-ino House, which was rationalized in production and was quickly assembled on-site thanks to the prefabricated elements, contained minimum building components.
L’Esprit Nouveau

Returning to Paris in 1917, Corbusier started painting next to Amédée Ozenfant, a renowned painter. Corbusier defended his ideas with the articles they wrote in the magazine “L’Esprit Nouveau” (New Spirit in French) together with Ozenfant.
Jeanneret wrote his writings under the pseudonym “Le Corbusier” and became famous with this name.
He opened an architecture studio with his cousin in 1922. With the participation of Charlotte Perriand in the studio, they started to design furniture.
Architectural Philosophy and Principles
Le Corbusier had a phenomenal architectural philosophy that continues to inspire and shape the design world.
In 1923, he published his book “Toward a New Architecture“, which is a kind of architectural manifesto. In this book, he emphasized the beauty of mass production and machine houses, as well as the importance of functionality. Instead of traditional decoration and adornment, he defended simple and white facades.
The architect summarized his architectural understanding into 5 distinct principles. These principles served as a guiding framework for his designs and other many modernists. In this framework, he emphasizes functionality, simplicity and harmony with nature.
Next section, we’ll take a detailed look at each of Le Corbusier’s 5 points of architecture.
5 Points of Architecture
1. Pilotis
Le Corbusier advised lifting buildings off the ground using pilotis, which are slender columns. By this means, he created an open space beneath the structures. This open space allows for better airflow, natural light and an uninterrupted flow of movement.
2. Ribbon Windows
The second principle of architecture is ribbon windows, aka horizontal windows. These windows span from one end to the other end of the facade.
Ribbon windows don’t only allow ample natural light but also provide stunning panoramic views of the surrounding environment.
3. Free Plan
The free plan concept is another principle of Le Corbusier. It eliminated load-bearing walls to allow for flexible and adaptable interior spaces. This results in creative freedom in arranging furniture and spaces as well as dynamic layouts.
4. Free Facade
Le Corbusier’s architecture wouldn’t be described without the free facade principle. He emphasized the independence of the exterior walls from the structural system.
Separating the facade from the structure, he gained the freedom to design facades with different materials and architectural expressions. This ensures more visually captivating buildings.
5. Roof Garden
The last principle of Le Corbusier’s architecture is the roof garden. Corbusier believed in the importance of integrating nature into his designs.
He often included terrace gardens. Occupants could enjoy green spaces and connect with the outdoors even if they are at the roof level. They can enjoy a peaceful retreat and harmonious extension of the living environment without leaving the structure.
Le Corbusier’s architectural understanding is more than these five points. He embraced the use of raw materials, such as reinforced concrete and steel.
He believed that architecture should prioritize functionality over ornaments, just like other modernists. A structure should meet the needs of its occupants while looking aesthetically attractive.
Moreover, he often incorporated architectural design and natural elements. He always tried to create a harmonious connection between the built environment and the natural environment.
All these Le Corbusier principles and philosophy have influenced modern architecture and a great number of architects worldwide.
Famous Le Corbusier Buildings & Projects
We can see the philosophy and architectural understanding of Corbusier in his famous works. In the following paragraphs, we’ll learn how he implemented his visionary ideas into structures.
1. Villa Savoye
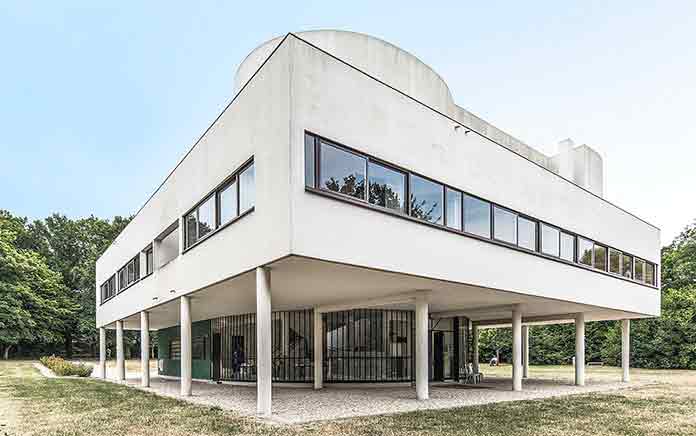

Designed in 1929, Villa Savoye is one of the most celebrated Le Corbusier works where 5 principles of architecture are clearly seen. It’s a masterpiece of modern architecture.
The structure rising over the pilotis has wide ribbon windows and a free plan setup. Inside, there is a ramp that continues uninterrupted from the ground floor to the terrace roof.
Villa Savoye is a house identified with Le Corbusier’s life machine concept. The building, which is open to visitors today, was included in the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2016.
2. Ville Radieuse
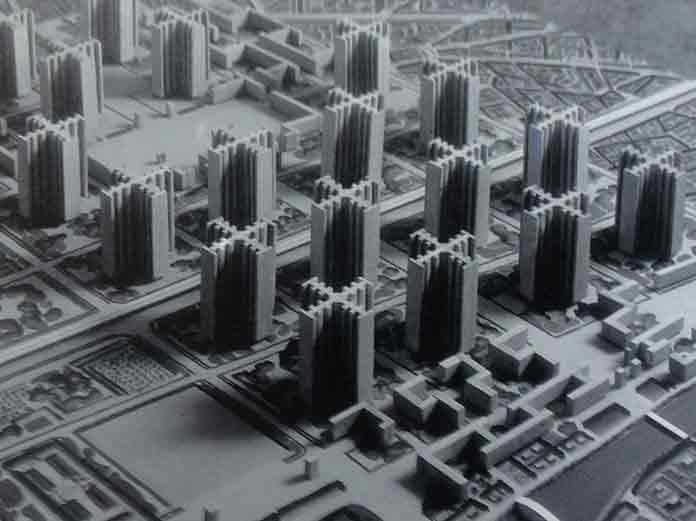

Corbusier published his Radiant City (La Ville Radieuse) project in 1935. According to his ideal city understanding, Corbusier divided the residential areas base on the size of the families.
In his opinion, crowded families, not the wealthy, should live in big houses. A clean city could create clean societies.
The concept city, which he designed in the light of these ideas, was a project that Corbusier created by cranking his design approach up a higher scale.
There were standardized production systems and building types, functional urban areas and living spaces interwoven with green. The business and commercial area, consisting of high skyscrapers in the center, was connected with transportation networks to other zones such as entertainment and housing.
Although this project remained in theory, many modern cities designed have been fed by the idea of the Radiant City.
3. Unide d’Habitation
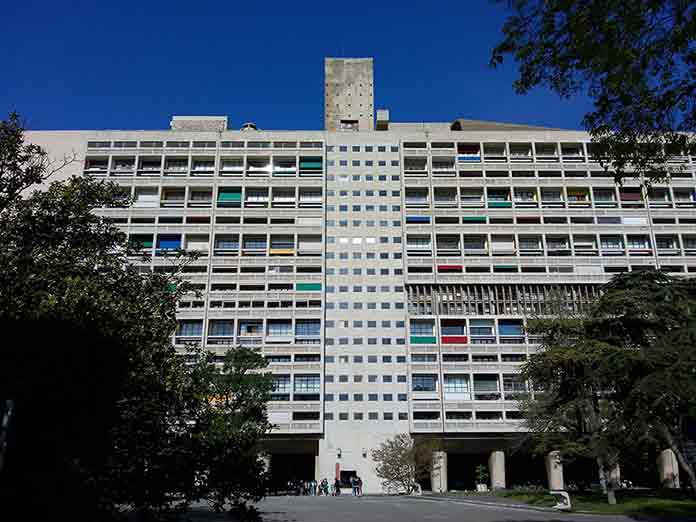

When World War 2 ended, Corbusier produced social housing projects. The most famous of these Le Corbusier works was Unite d’Habitation. He designed this structure as a solution to the lack of housing and economic problems which occurred after the war.
In this mass housing project, which is one of the most important examples of Brutalist architecture, there are rich spaces where people can satisfy their daily social requirements.
Its total capacity is 1600 people and it is produced for the working class. So the working class could have the same life as the bourgeoisie class.
Other Most Important Le Corbusier Works
- Unite d’Habitation
- Villa Savoye
- Weissenhof House
- Ronchamp Chapel (Notre Dame du Haut)
- Pencap Palace of Assambly
- Villa La Roche
- Dom-ino House
- National Western Arts Museum
- Philips Pavillion
- Firminy Saint-Pierre Church
Final Thoughts on Le Corbusier
The visionary architect Corbusier has left a memorable mark on the world of architecture and design. He has shaped the built environment through his innovative ideas, groundbreaking projects and steady principles.
His early life and education provided a solid foundation for his architectural journey. He put “Five Points of Architecture”, which are pilotis, free plan, free facade, ribbon windows and terrace garden, at the center of his architectural philosophy.
Implementing these principles, he designed many recognizable projects, including Villa Savoye, Notre-Dame du-Haut, Chandigarh Capitol Complex and Unite d’Habitation.
Beyond architecture, his influence extended to urban planning, furniture design, and more. He had ideas to reshape cities, design innovative furniture, and improve the architecture-human body relationship (“the Modulor”).
Died in 1965, he also founded the Le Corbusier Foundation before his death to donate his drawings and library. We remember him with respect and longing.
Thank you for joining us on this enlightening journey through his life, works, and architectural legacy.
FAQ
A: Le Corbusier, alias Charles-Édouard Jeanneret, was a renowned Swiss-French architect, designer, and urban planner. He is widely regarded as one of the pioneers of modern architecture.
A: Le Corbusier is famous for his leading contributions to modern architecture. He is renowned for his innovative design principles, known as the “Five Points of Architecture,” which emphasized functionality, simplicity, and harmony with nature.
He is also famous for designing iconic buildings like Villa Savoye, Unite d’Habitation and Notre-Dame-du-Haut. Additionally, Le Corbusier’s ideas on urban planning, his furniture designs, and his overall visionary approach have left a lasting impact on the field of design and architecture.
A: The five Points of architecture, proposed by Corbusier, are pilotis (elevated columns), a free plan, a free facade, ribbon windows and a roof garden. These principles aimed to maximize space, functionality, and harmony with nature.
A: Yes, he created iconic pieces like the LC4 Chaise Lounge, LC2 and LC3 sofas, and the LC1 Sling Chair, known for their combination of functionality and aesthetics.




















